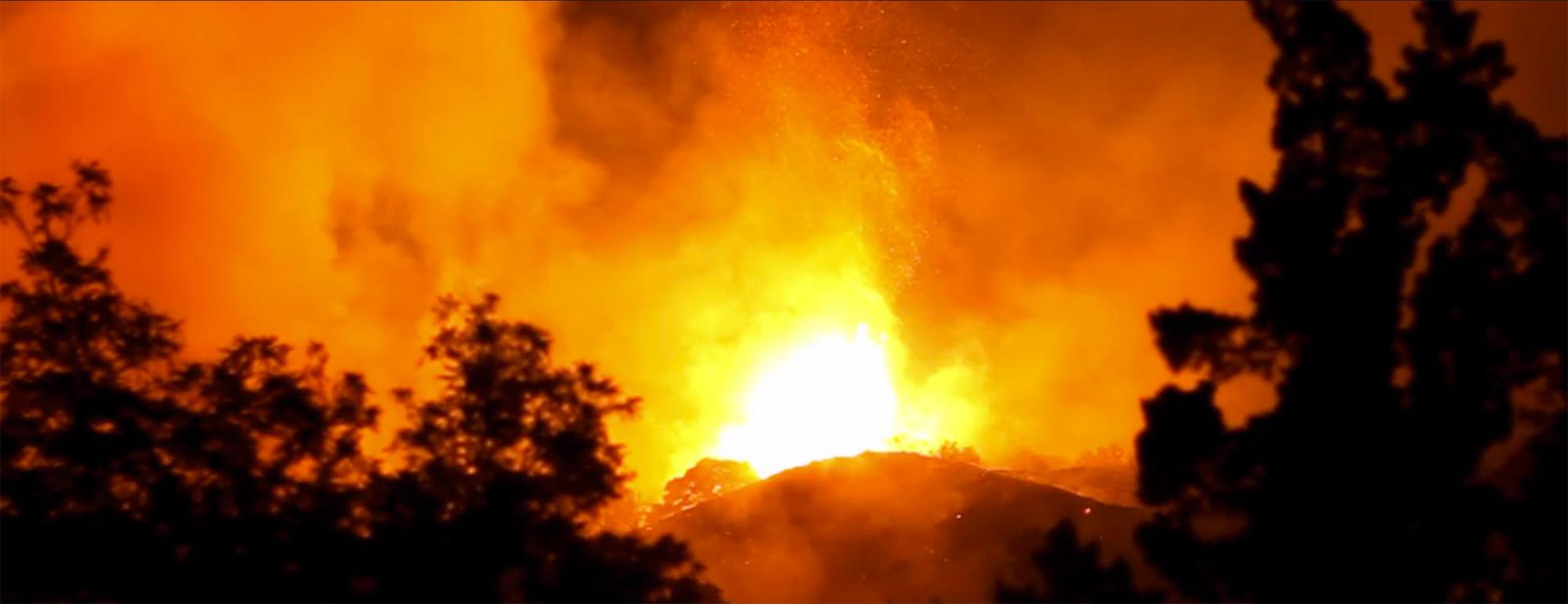
In the small hours of Oct. 8, 2017, Geraldine Calderon woke to feed her baby and smelled smoke.
“It’s a life-changing experience when you’re getting your baby out of bed at 3 in the morning and, you know, driving her through a highway where you can’t really see anything but flames in front of you,” said Calderon, an emergency room physician at Ukiah Valley Medical Center, in a videotaped interview for the UC Davis Environmental Health Sciences Center.
As Californians have fled ferocious wildfires in recent years, UC Davis scientists, veterinarians, physicians and teachers have also been responding to that trauma: treating people and animals, investigating the effects on mental and physical health, and trying to discover what the future might hold as wildfires burn into towns and suburbs.
WHAT-NOW for public health
Burn specialists at UC Davis Health treated 15 adult patients injured during the 2018 Camp Fire.
A year earlier, the Sonoma/Napa fires inspired Irva Hertz-Picciotto, professor of public health sciences and director of the Environmental Health Sciences Center at UC Davis, to develop the Wildfires and Health: Assessing the Toll in NorthWest California (WHAT-NOW) survey.
"I personally wanted to find a way to address what was going on with the resources of our center,” said Hertz-Picciotto.
More than 2,000 households and almost 7,000 people in 16 counties have responded to the online survey. Questions address peoples’ experiences during and after the fires: losses of people, pets and property; health problems, including respiratory problems, infections and mental health; and in collaboration with local governments, immediate and future needs of fire survivors, evacuees and others.
Initial survey results show that stress and anxiety are the most commonly reported symptoms, continuing for months after the events, Hertz-Picciotto said. Ongoing respiratory problems were also reported in both otherwise healthy people and in susceptible groups, such as people with asthma. Susceptible groups reported particularly high rates of respiratory symptoms.
“We do see that even people who don’t have prior respiratory problems are reporting pretty serious respiratory effects in the immediate aftermath — with asthmatics it’s four times higher,” she said.
“We do see that even people who don’t have prior respiratory problems are reporting pretty serious respiratory effects in the immediate aftermath — with asthmatics it’s four times higher.” — Irva Hertz-Picciotto
Hertz-Picciotto plans to follow the survey cohort forward over time. Most studies of the health impacts of fires focus on the short term. But respiratory diseases and mental health issues may take years to manifest.
Rebecca J. Schmidt, assistant professor of public health sciences, is leading the B-SAFE, Bio-Specimen Assessment of Fire Effects, study. B-SAFE is a longitudinal study following a group of women who were exposed to wildfire smoke in 2017 while pregnant or just before becoming pregnant, and their babies.
“There are a lot of concerns if you’re pregnant during these wildfires, we don’t know what’s in the smoke and also there’s a literature on the effects of stress in pregnancy. So we thought it was important to take a look at women who were pregnant during the fire emergency and also who became pregnant right afterwards,” Schmidt said.
Schmidt’s team has collected placenta and cord blood samples and is collecting hair and nail clippings, which can record such things as stress hormones and heavy metal exposure. They are also collecting saliva from the babies to examine markers of exposure. She hopes to be able to follow these children forward to study whether they have later health effects.
Hertz-Picciotto and Schmidt plan to extend their studies to include those affected by 2018 Camp Fire as well.
Clues from nonhuman primates
Clues to future respiratory problems could come from our close relatives. In the early summer of 2008, Professor Lisa Miller realized she had a natural experiment on her hands. Wildfire smoke had invaded the Davis region, including the California National Primate Research Center, or CNPRC, at UC Davis, where hundreds of rhesus macaque monkeys live in large outdoor corrals. Juvenile monkeys born earlier that year were exposed to poor air quality over several days.
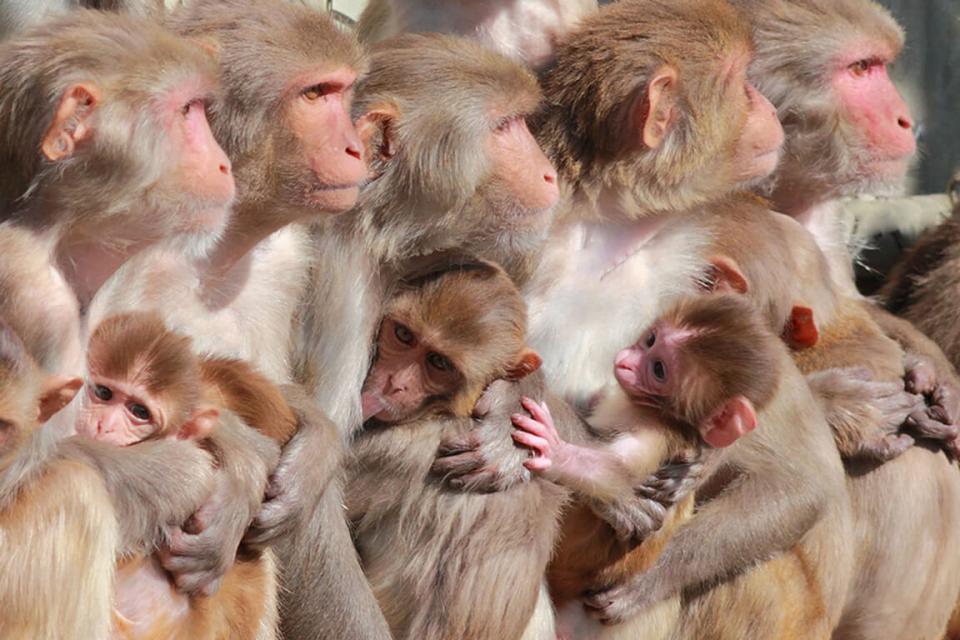

“It was a perfect storm of poor air quality in the valley and young animals living outdoors,” said Miller, professor of anatomy, physiology and cell biology at the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine, who leads the Respiratory Diseases Unit at the center. Researchers at the CNPRC work with macaques to study diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Based on monitoring data from the California Air Resources Board, smoke pollution in Davis in 2008 was similar to that seen in 2018, Miller said. However, monkeys living outdoors were exposed around the clock, while humans can shelter indoors. With funding from the board, Miller has followed the monkeys born in 2008 over several years, comparing them to animals born in 2009 who were not exposed to smoke as juveniles. A study published in 2017 describes their status at 3 years old; Miller and colleagues are working on data from animals at 8 years.
“We thought we would see asthma, but we didn’t,” at 3 years, Miller said. “But we did see changes in overall lung volume.” The smoke-exposed juveniles had smaller and less compliant, or “stiffer” lungs, Miller said. The condition looks more like COPD — typically seen in humans who are heavy smokers — than asthma, she said.
What’s in that ash?
Just what’s in the smoke and ash when you incinerate hundreds of houses? Smoke from wildland fires has been characterized, but recent fires have destroyed entire residential neighborhoods — and modern homes contain a wide variety of chemicals, from plastics, pesticides and cleaning products to rare metals in computers and other electronic devices. Following the Sonoma fires, UC Davis scientists launched efforts to understand just what’s going into ash and air.
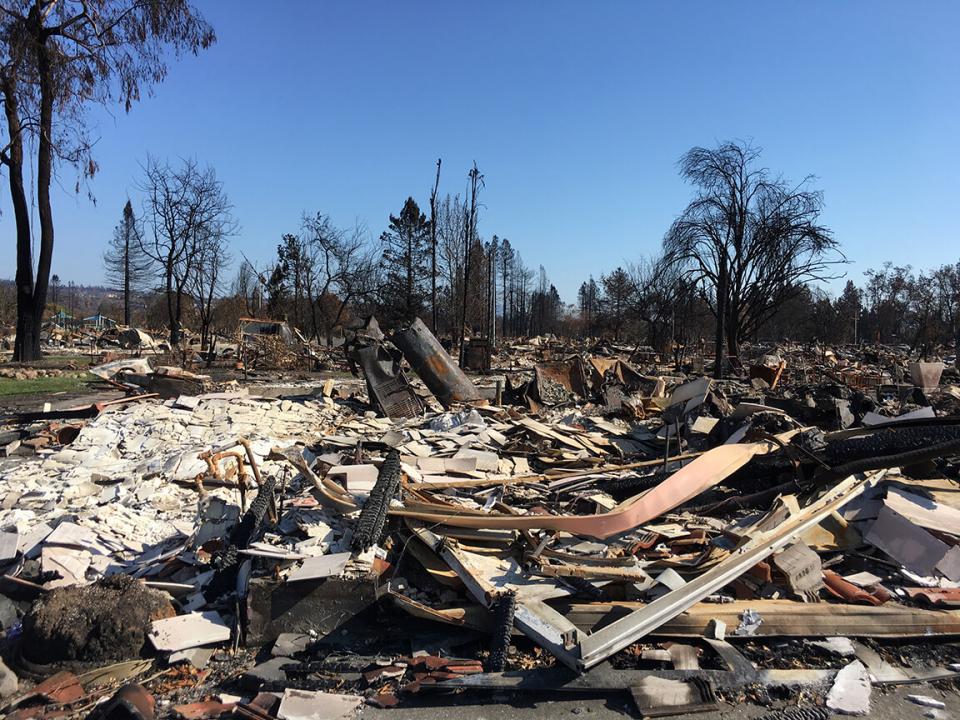

Keith Bein, a scientist at the UC Davis Air Quality Research Center, sampled smoke from the 2017 fires in his Oakland backyard. It gave him the idea to build a mobile sampling system, powered by Smart Car electric vehicles, that he can load on a flatbed trailer and take out into the field. Although safety rules limit researchers’ access while fires are burning, Bein has been able to collect data from areas burned in 2017 and 2018.
Gabrielle Black, a graduate student working with Professor Tom Young in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, collected ash samples from wildlands and residential areas burned in 2017.
With Michael Denison and Christoph Vogel in the Department of Environmental Toxicology, Black and Young have been teasing out the mix of compounds and looking for any trends.
The studies are ongoing. The team did find a number of compounds in ash from houses that were not found in ash from the state park. Both sets of samples contain dioxin-like compounds and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, chemicals known to be formed in combustion.
“We do have evidence of many chemicals in the residential ash samples,” Young said. “But so far, that stuff doesn’t seem to have any biological activity over what we expect to see in ash.”
“We do have evidence of many chemicals in the residential ash samples, but so far, that stuff doesn’t seem to have any biological activity over what we expect to see in ash.” — Tom Young
There’s also concern about chemicals finding their way into the food supply. Backyard chickens, in particular, could pick up contaminants as they scratch and peck the dirt. California residents can get their hens’ eggs tested for free in a study led by Maurice Pitesky, a cooperative extension specialist based at the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine.
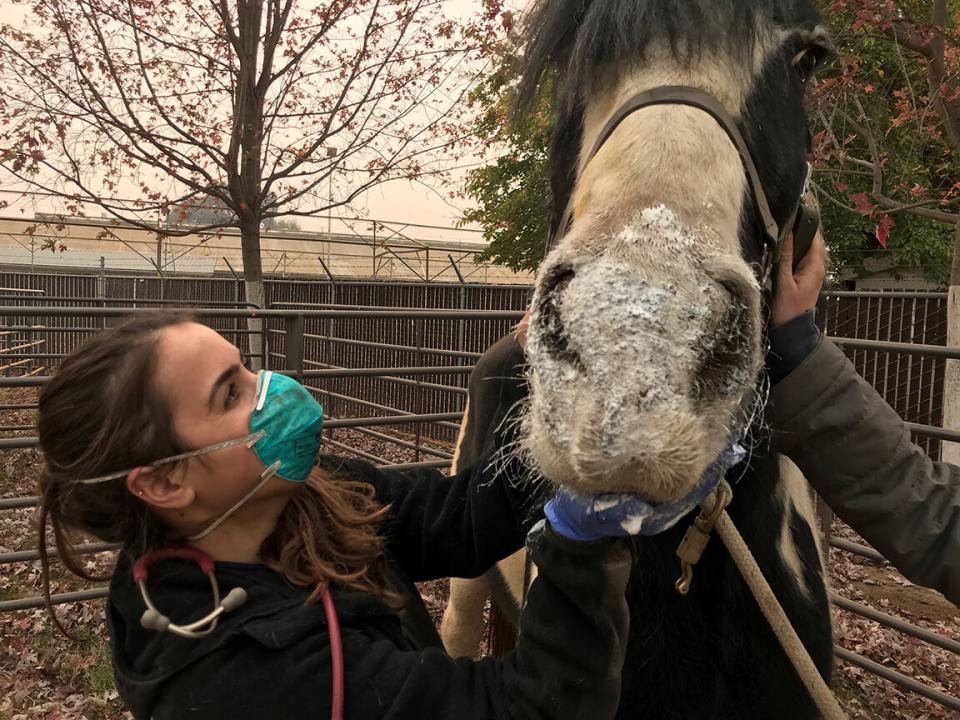
Treating animals impacted by wildfires
While human health is impacted by wildfires, animals need help too. Early on Nov. 8, 2018, news started coming of a fire moving fast in high winds toward the town of Paradise.

“When you’re in the business we’re in, that’s when you know,” said John Madigan, director of the Veterinary Emergency Response Team, or VERT at UC Davis.
Madigan knew there would be animals in need of help and began collecting his team. On Nov. 10, the state Office of Emergency Services asked VERT to deploy to the Butte County Fairgrounds. While the Camp Fire still raged, teams led by Madigan and veterinary faculty members Lais Costa and Emily Berryhill evaluated and treated hundreds of animals for injuries including stress, dehydration and burns.
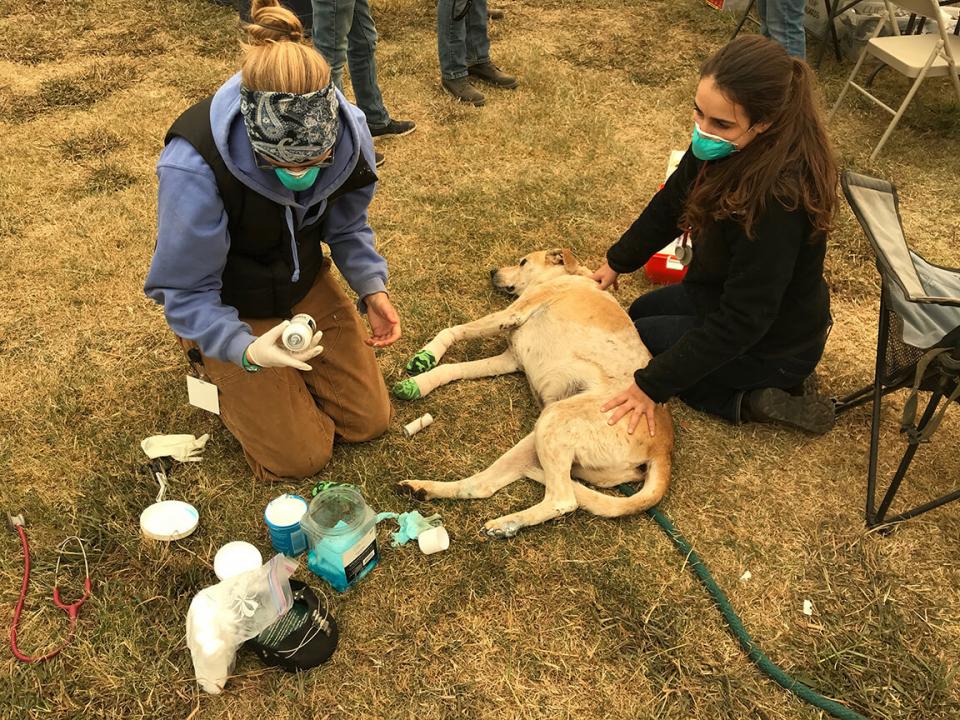

Nearly 70 animals including cats, goats, pigs, a donkey, a llama, several horses, a mini horse, a ewe, chickens, a goose, ducks, goldfish, koi, a tortoise and even a bobcat were brought to UC Davis for treatment during the 2018 Camp Fire.
“First-degree burns took only a few days to heal, while more severe burns required weeks to months of care,” said Steven Epstein, chief of the Emergency and Critical Care Service for the hospital’s Small Animal Clinic.

Fifty-five student volunteers and 10 veterinarians, including Bret McNabb, Richard Pereira, Maurice Pitesky, Michelle Hawkins, Monica Aleman, Charlotte Easton-Jones and Fiona Wensley took part, working through the Veterans Day and Thanksgiving holiday weekends.
A second VERT team was sent to the Red Cross shelter for people and pets, located at the same fairgrounds. Madigan also led teams into the burned areas once they were cleared for safety to perform welfare checks and deliver food and water to animals sheltering in place. The team’s efforts were supported by generous donors to a specific VERT fund.
“We couldn’t do this work without the generous people who support our efforts in the field,” Madigan said. “The animals may not be able to say it in words, but thank you.”

Related Stories
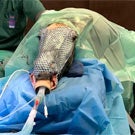
Healing Burned Animals With Fish Skins
UC Davis researchers are using Tilapia fish skins to help heal burns to both wild and domestic animals.

Guardians of the Genome
One in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer at some point in their lives, but through new discoveries at the genetic level the personal nature of cancer will eventually be what helps to beat it.
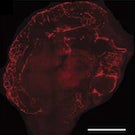
Minibrains Move a Step Closer to Helping Patients
UC Davis brain surgeon Ben Waldau has groundbreaking success growing parts of human brains.
Media Resources
Media contacts:
Andy Fell, UC Davis News and Media Relations, (530) 752-4533, ahfell@ucdavis.edu
Trina Wood, School of Veterinary Medicine, (530) 752-5257, tjwood@ucdavis.edu
